How to set up MT4grpc API image on the microK8s Kubernetes cluster from a blank virtual machine based on Debian 11
Log in to the virtual machine console
Use SSH for getting access to the virtual machine admin console. Have a look at details here.
Create SSH key.
Set up user with public ssh key on the virtual machine.
Use for connection via ssh:
ssh <username>@<virtual-machine-public-ip-address>Prepare microK8s cluster
Update operation system:
sudo apt-get update
sudo apt upgradeInstall Snap - packaging and deploying system
sudo apt install snapdInstall microk8s with Snap
sudo snap install microk8s –classic
MicroK8s creates a group to enable seamless usage of commands which require admin privilege. To add your current user to the group and gain access to the .kube caching directory, run the following two commands:
sudo usermod -a -G microk8s $USER
sudo chown -f -R $USER ~/.kubeRe-enter the session for the group update to take place.
Now you can check the status:
microk8s status --wait-ready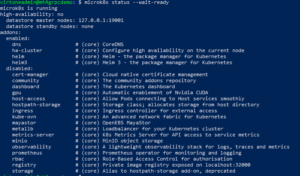
Curently we have clean microk8s cluster
microk8s kubectl get all --all-namespaces
Kube-system is a internal kubernetes namespace.
Create MT4 grpc API microservice
Apply new deployment to the cluster
microk8s kubectl apply -o json -f - <<EOF
{
"apiVersion": "apps/v1",
"kind": "Deployment",
"metadata": {
"name": "mt4grpc",
"labels": {
"app": "mt4grpc"
}
},
"spec": {
"replicas": 1,
"selector": {
"matchLabels": {
"app": "mt4grpc"
}
},
"template": {
"metadata": {
"labels": {
"app": "mt4grpc"
}
},
"spec": {
"containers": [
{
"name": "mt4grpc",
"image": "mtapiio/mt4grpc",
"env": [
{
"name": "GrpcWeb",
"value": "false"
}
],
"ports": [
{
"containerPort": 80
}
]
}
]
}
}
}
}
EOF
Now we can see microservice in the pod.
microk8s kubectl get all
You are able to check app logs, by using specific pod name
microk8s kubectl logs pod/mt4grpc-7c9c456df8-t7wwh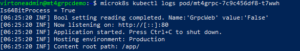
Create external entry point to the MT4 grpc service
Enable ingress NGNIX for microk8s
microk8s enable ingress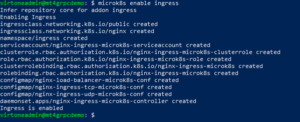
Enable cert manager for microk8s
microk8s enable cert-managerCreate ClusterIssuer object. It provides automatic Let's Encrypt ssl setificate management
microk8s kubectl apply -o json -f - <<EOF
{
"apiVersion": "cert-manager.io/v1",
"kind": "ClusterIssuer",
"metadata": {
"name": "lets-encrypt"
},
"spec": {
"acme": {
"email": "<your email>@mail.com",
"server": "https://acme-v02.api.letsencrypt.org/directory",
"privateKeySecretRef": {
"name": "lets-encrypt-priviate-key"
},
"solvers": [
{
"http01": {
"ingress": {
"class": "public"
}
}
}
]
}
}
}
EOFCreate kubernetes service, which would make mt4api discoverable inside the cluster
microk8s kubectl apply -o json -f - <<EOF
{
"apiVersion": "v1",
"kind": "Service",
"metadata": {
"name": "mt4grpc"
},
"spec": {
"selector": {
"app": "mt4grpc"
},
"ports": [
{
"protocol": "TCP",
"port": 8888,
"targetPort": 80
}
]
}
}
EOF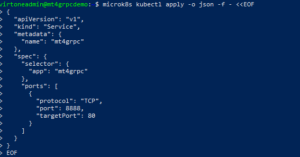
You can check that cluster service points to the current pod (current instance of mt4grpc api)
microk8s kubectl describe service/mt4grpc
Endpoint is the current pod (container instance)
Create ingress service. This is service for accessing internal kubecrnetes service from outside the cluster.
Put you domain name into spec/tls/hosts section and spec/rules/hosr section
microk8s kubectl apply -o json -f - <<EOF
{
"apiVersion": "networking.k8s.io/v1",
"kind": "Ingress",
"metadata": {
"name": "https-ingress",
"annotations": {
"cert-manager.io/cluster-issuer": "lets-encrypt",
"nginx.ingress.kubernetes.io/upstream-hash-by": "$remote_addr",
"nginx.ingress.kubernetes.io/backend-protocol": "GRPC"
}
},
"spec": {
"ingressClassName": "nginx",
"tls": [
{
"hosts": [
"test2.mtapi.be <--- replace it by your domain"
],
"secretName": "mt4grpc-ingress-tls"
}
],
"rules": [
{
"host": "test2.mtapi.be <--- replace it by your domain",
"http": {
"paths": [
{
"path": "/",
"pathType": "Prefix",
"backend": {
"service": {
"name": "mt4grpc",
"port": {
"number": 8888
}
}
}
}
]
}
}
]
}
}
EOFTroubleshooting
You can check ingress logs by this command:
microk8s kubectl logs pod/nginx-ingress-microk8s-controller-xtzdv -n ingressYou can take pod name from
microk8s kubectl get all --all-namespaces
This is how correct ingress enabling looks like:

This is how correct GET request looks like:

This is how correct GRPC request looks like:
